



|

|

|
|
|
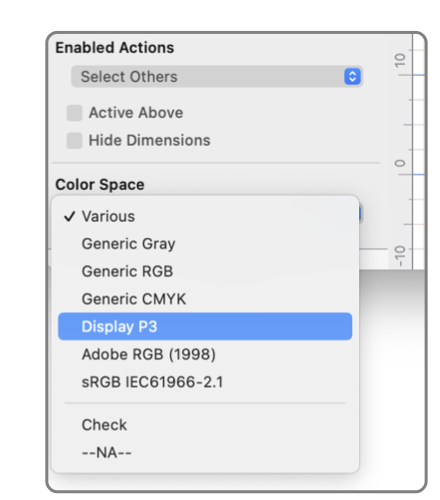
Layer Table EazyDraw is a color managed drawing application. Both Color Model and Color Space management is provided for individual graphics, graphic layers, and relavent export formats. Layer color management and inspection is found near the bottom of the layers inspector. Color Model is the mathematical method describing colors. Computer applications represent colors as tuples of numbers. For example, the RGB model represents a color as three numbers one each defining Red, Green, and Blue. Three color models are supported, RGB, CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black), and Gray. Internal representation will often add one more value to the number tuple to represent opacity. Color Space is an additional level of detail used with an electronic display. A Color Model is used in combination with a mathematical model called a color profile. Technology advancements of the 2010 - 2016 era have made Color Space an important aspect for content for web and computer application graphics. For most users especially Mac users the only thing to understand is to use Display P3 color space. The more discerning user may study this topic, it is well documented on the World Wide Web. Summary Tips: Do not use Generic RGB. Use Display P3 if the audience is Mac or Apple mobile devices. Use sRGB IEC61966-2.1 if the audience is wider than Apple users. The popup menu at the bottom of the layers Inspector is used to inspect or manage the color space for the layer. CMYK color model is relavent for professional printing. Professional printers normally require CMYK. In most cases RGB will be the color space used for computer drawing, this is the space rendered on the computer monitor. CMYK will result in different hues and colors, but these slight differences then result in a truer color on high quality printing presses. CMYK for personal use is now much more prevalent with home use photo quality printers. Mapping to CMYK may provide improved appearance when printing drawings to a photo-quality printer on high quality paper.
Bitmap images also require a defined Color Space. If there are images on a layer, the reported color space state includes the color spaces of all images on the layer. Graphic Details inspector for images, the quality tab, support color space inspection for individual images. Whereas monitors emit light, inked paper absorbs light, leaving the remaining components reflected to generate a color. Cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (K) pigments serve as the absorbing filters of the printed page. Each subtracts varying degrees of red, green and blue from white light to produce a gamut of spectral colors. Each of these color generating techniques will generate millions of shades and hues of colors - but not all possible colors. Contrary to intuition, the possible colors generated by additive (RGB) and subtractive (CMYK) techniques are not the same. The differences between colors generated by the two techniques are subtle but conversion from RGB to CMYK will produce quite noticeable color shifts on the viewed artwork. The macOS system color picker provides a component slider view that allows colors to be generated with a specific color space. When exporting PNG, TIFF, and EPS it is possible to map all colors on a drawing, rather than individual layers, to a particular color space. This mapping is temporary and does not alter the color shades for the master drawing. This may be a more convenient technique to manage color space for printing or submission to electronic pre-press process. It is possible to determine the Color Space for a specific color from the associated inspecting color well. Pause the cursor over a color well and a tool-tip display will indicate the exact details of the color on your drawing. This tip will indicate CMYK, or RGB and the specific component values. NOTE: This popup menu reflects the status of the layer or layers selected (highlighted) in the list above. It does not reflect the current status of a printed drawing which includes all visible layers. This is a bit confusing, but when considered carefully it provides the best inspection logic for indicating and managing the current status of a drawing. |